 Conference
Conference
From the Ruins of Preservation
A Symposium on Rethinking Heritage Through Counter-Archives
Symposium
11–12 July 2019

Organisers: Rodney Harrison (AHRC Heritage Priority Area Leadership Fellow/Professor of Heritage Studies at the UCL Institute of Archaeology) and Mirjam Brusius (Research Fellow in Colonial and Global History, German Historical Institute London)
Venue: German Historical Institute London
Confirmed Keynote Speakers: Rachel Ama Asaa Engmann (Assistant Professor of African Studies, Hampshire College), Trinidad Rico (Director of Cultural Heritage and Preservation Studies, Rutgers University) Karen Salt (Director of the Centre for Research in Race and Rights (C3R), University of Nottingham)
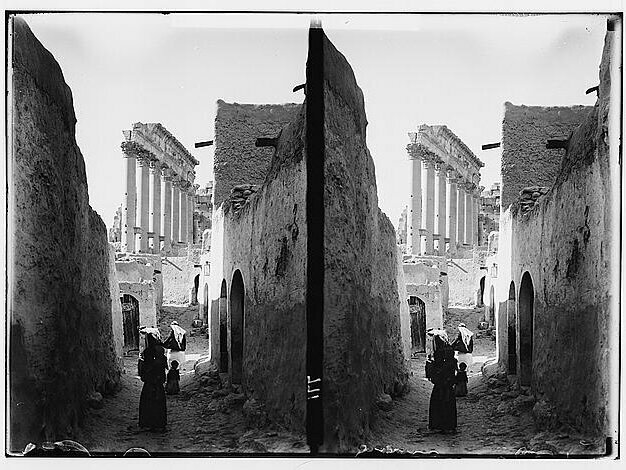
Colonial legacies in heritage preservation have intersected and clashed with local realities since their inception. Heritage sites have often been created by way of processes which segregate them both temporally and geographically from the contemporary world, and the people who live with and amongst them. This might result in restrictions of habitation and cultivation, religious and ritual practice, and the removal of entire local settlements from inside and around natural and cultural heritage sites. Individuals and communities, however, have always had their own ways of preserving and engaging with material and immaterial significances. Objects, places and landscapes were and are embedded and reactivated in the domains of contemporary life. These realities defy and challenge the disciplinary baggage, canons and categories as well as prevailing methods, discourses, concepts and practices of heritage studies, which in many cases have proved unhelpful in engaging such records outside of “the archive” as it is conventionally understood.
The problem of adequately engaging the histories of these intersections has been exacerbated by methodological challenges. Historians have long ignored the gaps and unspoken emotions and bodies in written and visual archival sources. Visual analyses often lack the methods to engage with different iterations of the diverse and heterogenous agencies of both humans and nonhumans outside of the scope of official archives—the locals going about their lives in ancient ruins; the workers who labour on archaeological excavations; those often nameless individuals who serve as human scales next to an excavated building; the local guides who help “open up” landscapes to preservationists; or the agencies and affordances of forms of material culture themselves. Due to a turn against the forms of authority empowered in conventional archival sources, critical heritage studies have largely denied the usefulness and significance of archives for the study of such non-official forms of heritage preservation, which has led to the de-privileging of historical and visual analysis. This frustration has resulted in a general turning away from such sources by researchers within heritage studies to focus on contemporary issues, and their accompanying methods, especially “oral history” and ethnography. However, this move has frustrated historians who have seen heritage studies as a field in which the historical contexts of the contemporary phenomena which such scholars study has been effectively written out of the picture.
This conference presents a methodological intervention into reductionist preservation histories by developing a new diachronic, more diverse vocabulary and directions for future research in and on this field. Reconstructing new histories and viewpoints in order to re-examine the “ruins of preservation” it aims to rethink the varied agencies which surround both natural and cultural heritage preservation practices through new conceptual and methodological approaches. Re-engaging such histories is not only important in building a new historical approach to heritage, but will also help researchers to reconceptualise and recontextualise contemporary heritage phenomena. By re-centring the discourse about “heritage” to examine specific non-state practices through such methods we also seek a more nuanced and effective understanding of how preservation has been determined over time and from different perspectives.
Call for papers (PDF file)
Conference programme (PDF file)
Conference report (PDF file), published in: GHIL Bulletin 42 (2020), Vol 1
Conference website at heritage-research.org
This event was streamed live and is now available here: